-
Top Software Picks for Supply Chain Managers

In the rapidly evolving world of commerce, software tools have become indispensable to modern supply chain management. These tools not only streamline operations but also enhance decision-making processes, allowing managers to respond more effectively to dynamic market conditions. The integration of advanced software solutions helps in managing everything from inventory levels and supplier negotiations to logistics and customer service, ensuring a seamless flow from the manufacturer to the marketplace.
Supply chain managers face a myriad of challenges including inventory discrepancies, supply and demand fluctuations, and logistic inefficiencies. Effective software solutions can address these challenges by providing comprehensive visibility into every step of the supply chain. They enable predictive analytics, real-time data monitoring, and automation of routine tasks, which are crucial for improving accuracy and efficiency. This technological empowerment helps managers anticipate problems, optimize resources, and deliver solutions swiftly and effectively.
This article aims to guide you through the top software picks that stand out in managing complex supply chains. We will explore a variety of tools that specialize in everything from Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) to advanced scheduling and analytics. Each tool will be examined for its features, benefits, and the specific supply chain challenges it addresses. Our goal is to provide insights that will help supply chain managers make informed decisions about the software solutions that best fit their operational needs.
ERP Systems: The Backbone of Supply Chain Management
SAP
SAP stands as a titan in ERP solutions, offering a robust platform that integrates various functions crucial for efficient supply chain management. From procurement to product delivery, SAP’s modules work seamlessly to ensure that every component of the supply chain is interconnected. This integration provides managers with a holistic view of operations, enabling better control and coordination across diverse activities. SAP’s real-time data processing capabilities ensure that decision-makers can act on the most current information, leading to more strategic planning and execution.
Oracle NetSuite
Oracle NetSuite provides a comprehensive suite of cloud-based ERP solutions designed to manage complex global supply chains. It excels in delivering real-time insights and automation across financial, customer relationship, and supply chain management. Oracle NetSuite’s platform is renowned for its scalability and flexibility, making it an ideal choice for businesses looking to grow and adapt in rapidly changing markets. Its capabilities include streamlined inventory management, efficient order processing, and integrated financial tracking, all of which contribute to enhanced supply chain transparency and productivity.
Microsoft Dynamics 365
Microsoft Dynamics 365 offers tailored solutions that enhance supply chain optimization through intelligent automation and data-driven insights. It combines CRM and ERP capabilities with Microsoft’s productivity applications, fostering better communication and collaboration across the supply chain. Dynamics 365 helps businesses anticipate customer demands, manage resources effectively, and improve overall service delivery through advanced analytics and machine learning. Its adaptability to changing business environments makes it a valuable tool for supply chain managers aiming to maintain competitive edges in their industries.
Inventory and Warehouse Management Solutions
Fishbowl Inventory
Fishbowl Inventory specializes in providing robust inventory management and order fulfillment solutions, particularly suited for small to mid-sized businesses. Its strength lies in its ability to offer advanced inventory control that integrates seamlessly with QuickBooks, making it a popular choice for companies looking to maintain precise records without the complexity of larger ERP systems. Fishbowl enables efficient tracking of stock levels, order status, and shipping processes, enhancing the accuracy and speed of warehouse operations. Its features like barcode scanning, asset management, and part tracking streamline the entire order fulfillment process, significantly reducing human error and improving overall productivity.
Infor CloudSuite
Infor CloudSuite offers specialized solutions for warehouse management that cater to industries with complex supply chain needs such as manufacturing, distribution, and retail. This cloud-based solution is renowned for its ability to optimize warehouse space and logistics through layout and process management tools that drive efficiency and reduce operational costs. Infor CloudSuite facilitates real-time inventory visibility, demand forecasting, and labor management, which are crucial for maintaining a responsive and flexible warehouse operation. Its capabilities extend to handling global inventory requirements and managing multiple warehouse locations effortlessly.
Manhattan Associates
Manhattan Associates is recognized for its robust solutions addressing the complexities of warehouse and inventory management on a global scale. Its platform excels in optimizing every aspect of the supply chain, from inventory sourcing to product delivery. Manhattan’s solutions are designed to enhance the agility and reliability of supply chain operations, accommodating fluctuations in demand and supply with advanced forecasting tools. Their warehouse management system (WMS) is particularly adept at boosting productivity by enabling multi-channel distribution and supporting complex fulfillment strategies. This makes it an ideal choice for large enterprises that require a high degree of scalability and customization.
Transportation Management Systems (TMS)
JDA Software
JDA Software, now part of Blue Yonder, offers comprehensive capabilities for planning and executing transportation logistics that streamline shipping processes and enhance freight management. JDA’s TMS solutions help businesses optimize their transportation schedules and routes, manage freight auditing, and execute payment systems, all while providing real-time tracking of goods. This integration of logistics processes ensures that companies can reduce transportation costs, improve carrier management, and enhance service delivery through predictive analytics and detailed performance reports.
Kuebix TMS
Kuebix TMS stands out for its ability to optimize transportation operations and reduce logistical costs through an accessible, cloud-based platform. Kuebix offers a range of features from rate comparison and shipment booking to freight management and analytics. Its user-friendly interface and integration capabilities with other ERP systems make it a versatile tool for companies looking to enhance their transportation efficiency. Additionally, Kuebix provides a community load match feature, allowing businesses to find the best rates and transportation modes for their shipping needs, thereby improving bottom-line savings.
Descartes Systems Group
Descartes Systems Group provides sophisticated solutions for logistics and supply chain management, focusing on improving the efficiency and reliability of transportation operations. Their TMS integrates logistics processes across planning, scheduling, and monitoring, facilitating seamless communication and documentation throughout the supply chain. Descartes is particularly strong in regulatory compliance management, ensuring that companies meet global shipping regulations and standards. By leveraging Descartes’ advanced network and real-time data, companies can enhance logistical planning, reduce transportation overhead, and improve overall supply chain performance.
Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) Software
Aspen Technology
Aspen Technology, often simply referred to as AspenTech, plays a critical role in production planning and schedule optimization. Its software solutions are designed to enhance operational efficiency in industries such as chemicals, energy, and engineering. AspenTech’s APS software excels at balancing supply and demand, optimizing production processes, and reducing costs through advanced simulation and analysis tools. This allows companies to predict potential disruptions and adjust schedules proactively, ensuring continuity and efficiency in production operations.
Plex Systems
Plex Systems offers robust capabilities in manufacturing and supply chain planning through its cloud-based ERP software. Plex helps manufacturers streamline their operations from the shop floor to the top floor, with real-time visibility into every aspect of production. Its APS features enable precise scheduling, inventory control, and quality management, integrating all these functions within a unified platform. This comprehensive approach helps businesses maintain lean operations and respond flexibly to market changes, enhancing overall supply chain resilience.
Kinaxis RapidResponse
Kinaxis RapidResponse stands out for providing agility in supply chain operations through its advanced planning platform. RapidResponse delivers real-time response capabilities and what-if analysis that empower businesses to manage multiple interconnected supply chain variables. With Kinaxis, companies can rapidly adjust to supply chain volatility and make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives. This responsiveness is crucial for businesses operating in fast-paced industries where market conditions can change abruptly.
Innovations in Supply Chain Software
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is increasingly being recognized for its potential to revolutionize supply chain transparency. By allowing data to be shared across a network of stakeholders without central control, blockchain provides an immutable record of transactions, which enhances traceability and reduces fraud. This technology is particularly impactful in sectors where provenance and authenticity are critical, such as pharmaceuticals and luxury goods. Implementing blockchain can significantly increase trust and efficiency in these complex supply chains.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming supply chain management by enabling predictive analytics and intelligent decision-making. These technologies analyze large volumes of data to forecast trends, anticipate demand, and optimize logistics. AI and ML can automate routine tasks, predict maintenance needs, and even suggest strategies to mitigate risks. Their growing role is crucial for developing more proactive and adaptive supply chain strategies.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) significantly impacts real-time tracking and monitoring within supply chains. IoT devices collect and transmit data from every corner of the supply chain, providing insights into everything from warehouse inventory levels to the temperature conditions of shipped goods. This level of monitoring enhances operational transparency, improves asset utilization, and reduces operational risks, making IoT an indispensable component of modern supply chain management.
Conclusion: Enhancing Supply Chain Efficiency
Choosing the right software is essential for modern supply chains to achieve efficiency, visibility, and competitiveness. From ERP systems like SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics to innovations in blockchain, AI, and IoT, these tools provide the capabilities needed to manage complex operations effectively. They allow companies to stay agile, make data-driven decisions, and meet the evolving demands of the global market. As technology continues to advance, the integration of these sophisticated tools will increasingly become a hallmark of successful supply chain management, ensuring that businesses not only survive but thrive in today’s competitive landscape.
-
Planning Perfection: The 4 D’s of Logistics

Logistics management is a dynamic and multifaceted field that relies on several key principles to ensure efficient operations. The 4 D’s of logistics – Design, Demand, Delivery, and Development – serve as a framework for guiding logistics management, supporting seamless supply chain operations and balanced distribution networks. These principles reflect the diverse nature of logistics, encompassing everything from strategic planning to technological integration and continuous improvement.
The 4 D’s represent critical aspects of logistics management. Design involves mapping out supply chains, distribution networks, and transportation routes, ensuring seamless operations. Demand focuses on forecasting needs, balancing supply and demand, and managing resources. Delivery encompasses distribution strategies, last-mile logistics, and performance metrics, ensuring efficient deliveries to end customers. Development involves continuous improvement, training and education, and sustainable practices, enhancing logistics performance and adaptability.
This article aims to explore each of the 4 D’s of logistics, delving into their specific roles and impact on logistics operations. It will examine how these principles guide logistics management, from network design to continuous improvement, supporting efficient operations. The article will also explore how the 4 D’s adapt to today’s logistics landscape, incorporating technological advancements, sustainable practices, and industry challenges.
D1: Design
Logistics Network Design
Logistics network design plays a crucial role in shaping efficient supply chains, distribution networks, and transportation routes. This involves mapping out the flow of goods from suppliers to manufacturers, distributors, and end customers. Logistics managers design networks that balance supply and demand, optimize transportation routes, and minimize lead times. This design process also includes managing relationships with various stakeholders, ensuring seamless coordination throughout the supply chain.
Facility Location
Facility location is another essential aspect of logistics design, ensuring efficient storage, warehousing, and distribution. Logistics managers strategically place warehouses, distribution centers, and fulfillment facilities to minimize transportation costs and lead times. This involves analyzing geographic proximity to suppliers, customers, and transportation networks, balancing efficiency with cost-effectiveness. By optimizing facility locations, logistics professionals support seamless supply chain operations and timely deliveries.
Technology Integration
Technology integration enhances logistics design, introducing real-time tracking, data analytics, and automation into operations. Real-time tracking provides visibility throughout the supply chain, allowing managers to monitor shipments and proactively manage potential disruptions. Data analytics leverages historical data and market trends to forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and enhance network design. Automation streamlines various logistics processes, from order processing to warehouse management, reducing human error and increasing efficiency.
D2: Demand
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting plays a crucial role in logistics, utilizing historical data and market trends to anticipate needs and balance supply and demand. Logistics managers analyze sales patterns, consumer behavior, and market trends to forecast demand accurately. This enables companies to adjust inventory levels, production schedules, and distribution strategies, ensuring a steady flow of goods throughout the supply chain. Accurate demand forecasting minimizes overstocking, reduces storage costs, and supports seamless logistics operations, adapting to changing market conditions.
Capacity Planning
Capacity planning manages logistics resources to ensure adequate supply meets demand. This involves assessing production capabilities, storage capacity, and distribution networks, balancing resources with anticipated demand. Logistics managers adjust production schedules, inventory levels, and transportation routes to accommodate varying levels of demand, maintaining efficient operations. Capacity planning helps avoid bottlenecks, prevents supply chain disruptions, and supports seamless logistics management, ensuring consistent product availability.
Seasonal Variations
Seasonal variations present unique challenges in demand, requiring logistics managers to adapt strategies to address fluctuations. These variations include holiday seasons, promotional events, and industry-specific trends that impact demand levels. Logistics professionals adjust inventory levels, distribution networks, and delivery schedules to accommodate these variations, maintaining efficient operations. By managing seasonal demand, companies avoid stockouts, minimize overstocking, and ensure timely deliveries, supporting seamless logistics throughout the year.
D3: Delivery
Distribution Strategies
Various distribution strategies contribute to efficient logistics operations, including direct delivery and hub-and-spoke models. Direct delivery involves shipping goods directly from manufacturers to end customers, minimizing intermediaries and reducing lead times. Hub-and-spoke models centralize distribution, with goods shipped to a hub before being distributed to customers via spokes. This model optimizes transportation routes, reducing costs and supporting efficient deliveries. Logistics managers select distribution strategies based on factors such as distance, cost, and delivery speed, ensuring balanced operations.
Last-Mile Delivery
Last-mile delivery is a critical component of logistics, ensuring timely and efficient deliveries to end customers. This stage involves transporting goods from distribution centers to consumers’ doorsteps, balancing speed with cost-effectiveness. Logistics managers optimize last-mile delivery by managing transportation routes, schedules, and carrier networks. The integration of real-time tracking technology enhances last-mile delivery, providing visibility and allowing for proactive management. Efficient last-mile delivery supports customer satisfaction, reduces delays, and enhances overall logistics performance.
Performance Metrics
Logistics uses performance metrics to measure delivery success, including delivery times, order accuracy, and customer satisfaction. Delivery times reflect the efficiency of distribution networks and transportation routes, providing insights into logistics performance. Order accuracy measures how accurately products are delivered, ensuring correct items reach customers. Customer satisfaction reflects the overall success of logistics operations, balancing speed, accuracy, and service quality. By regularly monitoring performance metrics, logistics professionals identify areas for improvement, optimize operations, and support seamless deliveries.
D4: Development
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement strategies play a crucial role in optimizing logistics performance. Six Sigma and lean management methodologies aim to minimize waste and variation, streamlining logistics processes. Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects and improving quality control, ensuring consistent product quality and enhancing customer satisfaction. Lean management emphasizes efficient operations, reducing costs and maximizing productivity. Continuous improvement strategies involve regular evaluations, identifying areas for enhancement, and implementing solutions to optimize logistics operations. This adaptability supports efficient supply chains and sustains long-term success.
Training and Education
Training and education are vital for developing logistics professionals, enhancing their skills and expertise. This includes comprehensive training programs that cover various aspects of logistics management, from supply chain coordination to technology integration. Education also encompasses ongoing learning opportunities, such as industry conferences, workshops, and certification programs. By investing in training and education, logistics companies equip their professionals with the knowledge needed to navigate complex industry challenges, supporting seamless operations.
Sustainable Development
Sustainable development practices are increasingly important in logistics, reducing carbon footprints and promoting eco-friendly solutions. This involves optimizing transportation routes to minimize emissions, utilizing electric vehicles, and adopting alternative fuels. Sustainable development also extends to warehousing, where companies implement energy-efficient lighting, recycling programs, and green building certifications. Logistics professionals integrate sustainable practices throughout supply chains, balancing efficiency with environmental responsibility. These practices not only benefit the environment but also appeal to environmentally conscious consumers, enhancing company reputations.
Conclusion: Planning Perfection in Logistics
The 4 D’s of logistics – Design, Demand, Delivery, and Development – form a comprehensive framework that guides logistics management. Design involves mapping out supply chains and integrating technology, ensuring efficient operations. Demand addresses forecasting, capacity planning, and seasonal variations, balancing supply and demand. Delivery encompasses distribution strategies, last-mile logistics, and performance metrics, supporting seamless distribution. Development focuses on continuous improvement, training, and sustainable practices, optimizing logistics operations. By integrating the 4 D’s, logistics professionals ensure efficient management, support global commerce, and adapt to changing market demands.
-
Logistics vs. Supply Chain: Understanding the Differences
In the bustling arena of modern businesses, supply chain and logistics emerge as the silent heroes, quietly propelling companies towards efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and heightened customer satisfaction. As we navigate through the complexities of today’s globalized market, the roles these elements play become increasingly indispensable. They are the cogs in the machine that ensure your latest gadget, your morning cup of coffee, and even the shirt on your back arrive just when and where they’re needed. However, a common haze often surrounds these terms, with many using them interchangeably. Let’s clear the air: while intertwined and symbiotic, supply chain and logistics are distinct entities, each with its own set of responsibilities and objectives.
Understanding the Supply Chain
Imagine a vast network, a web of activities, entities, information, and resources, all orchestrated to breathe life into a product or service. This is the supply chain. From the inception of raw materials to the moment a product lands in the hands of the end customer, the supply chain weaves through various phases – sourcing, production, transportation, storage, and delivery. It’s a complex ballet of moving parts, each critical to the final performance.
At its heart, supply chain management (SCM) is strategic. It’s not merely about pushing goods down the line; it’s about streamlining these processes to carve out efficiency, pare down costs, and elevate the customer experience to new heights. It’s a balancing act, aiming to ensure that every link in the chain operates harmoniously, minimizing waste and maximizing value. SCM takes a bird’s-eye view, overseeing the entire life cycle of a product, ensuring that each step is optimized not just for speed or cost, but for sustainability and quality.
Diving into Logistics
Logistics, often visualized as the lifeblood of the supply chain, focuses on the transportation, warehousing, and delivery aspects of the business world. Imagine logistics as the arms and legs of the supply chain, where the strategy decided by the brain (supply chain management) is put into action. This segment ensures that the goods are not just moved but are also stored and delivered in an orchestrated manner that aligns with customer demands and business objectives.
The primary mission of logistics management is to navigate the complex journey of products from warehouses to the end consumer in the most efficient, cost-effective way possible, without compromising the condition and quality of the product. This involves meticulous planning and execution across transportation routes, warehousing strategies, and delivery mechanisms to ensure that the right product reaches the right customer at the right time.
Key Differences and Similarities
While logistics and supply chain management are interconnected, understanding their distinct roles illuminates how businesses can optimize operations for better outcomes. The scope of supply chain management is vast, encompassing everything from product conception to the final delivery, including the strategic partnerships and processes that facilitate this journey. Logistics, however, zooms in on the actual movement and storage of goods, acting as the operational arm that executes parts of the broader strategy set by supply chain management.
This relationship highlights the interdependence between the two—without effective logistics, the strategic plans of supply chain management would remain theoretical. Conversely, logistics operations benefit from the overarching direction and optimization efforts of supply chain management, ensuring that logistics activities contribute to broader business goals.
The Strategic and Tactical Perspectives
Supply chain management and logistics differ not just in scope but also in their approach to improving business operations. Supply chain management adopts a strategic, long-term view, focusing on building a competitive advantage by enhancing efficiency and fostering innovation across the entire product lifecycle. This involves decision-making that affects the supply chain’s future direction, such as entering new markets, developing sustainable practices, or reconfiguring the supply network for resilience.
On the other hand, logistics hones in on the tactical, dealing with day-to-day operations and immediate challenges. It’s about solving the puzzle of getting products to their destination as efficiently as possible, whether through optimizing delivery routes, managing inventory levels, or selecting transportation modes. Despite these operational concerns, logistics aims to align closely with the strategic objectives of the supply chain, ensuring that every package delivered on time is a step towards greater customer satisfaction and operational excellence.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
The surge of technology has profoundly impacted both supply chain management and logistics, driving unprecedented improvements in visibility, efficiency, and sustainability. In the digital era, technology acts as the great enabler, allowing businesses to track and manage their operations in real-time, predict and respond to market changes with agility, and reduce their environmental footprint. Automated inventory management systems, for instance, have revolutionized how businesses track and manage stock levels, minimizing waste and optimizing storage costs. Advanced routing technologies have streamlined logistics operations, ensuring that transportation is both time and fuel-efficient, thus reducing carbon emissions and costs.
Supply chain visibility solutions stand out as a transformative advancement, offering businesses a panoramic view of their supply chain activities. These technologies enable companies to track goods from origin to delivery, identify bottlenecks, and respond proactively to disruptions. By integrating data analytics, businesses can now forecast demand more accurately, tailor their inventory accordingly, and enhance their overall operational resilience.
Practical Advice for Aspiring Entrepreneurs
For the aspiring entrepreneur, mastering the nuances of supply chain management and logistics can be a game-changer. The first step is strategic planning, where understanding the symbiotic relationship between supply chain and logistics can help in designing a business model that is both efficient and scalable. Adopting the right technologies is crucial; tools like cloud-based supply chain management software or logistics platforms can provide the agility and insight needed to make informed decisions quickly.
When it comes to logistics, entrepreneurs face a critical decision: to manage logistics in-house or outsource to third-party logistics (3PL) providers. This decision hinges on several factors, including cost, control, and complexity of operations. 3PL providers can offer expertise and economies of scale, particularly for startups looking to expand quickly without the burden of managing logistics operations. However, retaining control over logistics can offer greater flexibility and direct oversight for businesses with specialized needs.In conclusion, the distinctions and synergies between supply chain management and logistics underscore their collective importance in establishing a competitive, efficient, and customer-focused business. As the landscape evolves, integrating innovative technologies and sustainable practices into these domains is not just beneficial but essential for long-term success. Entrepreneurs who adeptly navigate these waters, leveraging the strengths of both supply chain and logistics while embracing the digital revolution, will not only streamline their operations but also set the stage for scalable growth and resilience in the face of future challenges.
-
Logistics Persona: Are You Fit for the Industry?

The logistics industry, a linchpin of global commerce, is a vast network that ensures the seamless movement of goods from the point of origin to the end consumer. It encompasses a wide range of activities, from the management of supply chains and transportation networks to warehousing and inventory control. As the global economy becomes increasingly interconnected, the role of logistics in facilitating trade, supporting economic growth, and meeting consumer demands has never been more critical. The rise of e-commerce, coupled with advancements in technology, has further amplified the complexity and scope of logistics operations, making efficiency, innovation, and reliability key drivers of success.
This dynamic and fast-paced environment requires a specific type of individual—the “logistics persona.” This persona is characterized by a unique blend of personal attributes, professional interests, and a skill set that aligns with the demands of the logistics sector. For those considering a career in this field, identifying with this logistics persona can be a strong indicator of potential success and fulfillment. The industry offers diverse opportunities but also poses unique challenges, making it imperative for individuals to assess their fitment with the logistical demands and lifestyle before embarking on this career path.
Core Traits of a Logistics Professional
The logistics sector values individuals who not only possess the technical know-how but also exhibit certain inherent traits that are conducive to success in this field:
- Adaptability: In an industry where change is the only constant—be it due to technological advancements, shifts in global trade policies, or changes in consumer behavior—being adaptable is crucial. Logistics professionals must be nimble, ready to pivot strategies in response to new information or emerging trends, ensuring the continuous flow of operations despite disruptions.
- Problem-solving Orientation: Every day in logistics presents a new set of puzzles to solve. Whether optimizing logistics routes to reduce delivery times, adjusting to last-minute changes in inventory, or finding cost-effective solutions to supply chain bottlenecks, a problem-solving mindset is indispensable. This trait drives logistics professionals to not just identify issues but to creatively and efficiently address them, ensuring operational continuity and customer satisfaction.
- Attention to Detail: The logistics process is intricate, with numerous elements needing to synchronize perfectly to achieve the desired outcome. A strong attention to detail is essential for managing these complexities, ensuring that shipments are accurate, inventory levels are meticulously maintained, and all documentation is complete and compliant. This meticulousness reduces errors, saves costs, and enhances the reliability of logistics operations.
Skill Sets That Thrive in Logistics
Complementing the core traits are specific skills that are particularly valued in the logistics sector:
- Analytical Thinking: The ability to sift through data, discern patterns, and derive insights is fundamental in logistics. Whether it’s analyzing shipment data to improve delivery routes, evaluating supplier performance, or forecasting inventory needs, analytical skills enable logistics professionals to make informed, strategic decisions that enhance operational efficiency and effectiveness.
- Effective Communication: The essence of logistics lies in coordination and collaboration. Effective communication skills are crucial for liaising with a diverse network of stakeholders including suppliers, customers, regulatory bodies, and internal teams. Clear and persuasive communication ensures that expectations are managed, objectives are aligned, and operations are executed smoothly across the supply chain.
- Technological Proficiency: With digital transformation reshaping the logistics landscape, proficiency in the latest technologies and systems used in SCM (such as WMS, TMS, and ERP systems) is vital. Understanding how to leverage these tools for better inventory management, route planning, and data analytics can significantly improve the efficiency and resilience of supply chain operations.
- Project Management: Logistics entails the execution of complex projects, from the rollout of new software systems to the opening of distribution centers. Skills in project management, including planning, execution, and monitoring, are essential for bringing these projects to fruition on time, within budget, and according to specifications, driving improvements across the logistics chain.
Professional Interests Aligned with Logistics
A career in logistics often starts with a spark of interest in the mechanisms that drive global trade and commerce. This interest can manifest in various ways, but there are common threads that tie aspiring logistics professionals together. One such thread is the fascination with the complexity and scope of global trade. Individuals drawn to understanding how products move across continents, the intricacies of customs regulations, and the strategies behind selecting trade routes often find logistics to be a perfect match for their curiosity.
Another significant area of interest is the commitment to sustainability within supply chains. As businesses and consumers increasingly prioritize eco-friendly practices, the logistics industry has become a critical player in implementing sustainable solutions. Those passionate about finding ways to reduce carbon footprints, minimize waste, and promote ethical sourcing see logistics as a field where they can make a tangible impact on environmental sustainability.
Furthermore, enthusiasm for technology-driven innovation is a strong indicator of a fit for the logistics sector. The industry is at the forefront of adopting cutting-edge technologies, from blockchain for enhancing transparency to drones for last-mile delivery. Individuals excited by the potential of such technologies to transform traditional logistics operations find a wealth of opportunities to innovate and drive change within the field.
These professional interests not only signal a natural alignment with logistics but also pave the way for fulfilling and impactful careers. Whether it’s by streamlining global supply chains, advancing green logistics initiatives, or leading technological transformations, individuals can leverage their passions to contribute significantly to the industry’s evolution.
Navigating the Logistics Career Path
Embarking on or transitioning into a logistics career is an exciting journey that requires strategic planning and action. The first step often involves formal education, where aspiring professionals can choose from a range of programs tailored to logistics and supply chain management. Degrees and certifications provide a solid foundation of knowledge and signal to employers a serious commitment to the field. However, education is just the beginning.
Building a robust professional network is equally important. Engaging with industry associations, attending logistics conferences, and participating in related forums can offer invaluable connections and insights. Networking not only opens doors to job opportunities but also provides mentors who can guide career development.
Gaining practical experience is another critical step. Internships and entry-level positions in logistics companies offer hands-on exposure to the industry’s challenges and best practices. These experiences are crucial for understanding the day-to-day realities of logistics roles and can significantly enhance employability. Volunteering for projects, even in unrelated positions, that can showcase relevant skills such as project management or analytical thinking, also adds valuable experience to a resume.
Continuous professional development is the key to long-term success in logistics. The industry’s fast pace requires professionals to stay abreast of new technologies, regulations, and best practices. Pursuing advanced certifications, attending workshops, and continuous learning through online platforms can help individuals grow their expertise and advance their careers.
Advancement opportunities in logistics are abundant for those who are proactive about their career development. From specialized roles in sustainability and technology to leadership positions managing entire supply chains, the logistics sector offers a diverse landscape of career paths. By aligning education, networking, and practical experiences with their professional interests, individuals can navigate their way to rewarding careers in logistics, making significant contributions to the industry and the global economy.
Self-Assessment: Is Logistics Right for You?
Determining whether a career in logistics aligns with your personal attributes and professional aspirations involves introspection and self-assessment. Consider the following questions to gauge your compatibility with the logistics field:
Do you thrive in fast-paced, dynamic environments? Logistics is constantly evolving, requiring professionals to adapt quickly to changes and challenges.
Are you a problem-solver who enjoys analytical tasks? Success in logistics often hinges on the ability to analyze data, identify inefficiencies, and devise effective solutions.
Can you manage complexity and multitask effectively? The logistics sector involves coordinating numerous elements simultaneously, necessitating strong organizational skills.
Do you have strong communication skills, and can you collaborate with diverse teams? Effective logistics operations depend on clear communication and teamwork across various departments and stakeholders.
Are you interested in technology and motivated to learn about new innovations? Technology plays a crucial role in logistics, from data analytics to automation and blockchain.
Do you feel strongly about sustainability and ethical business practices? Logistics offers opportunities to drive sustainability initiatives within global supply chains.
If you answered “yes” to most of these questions, a career in logistics might be a good fit for you. Interpreting these results as a strong alignment suggests that your traits and interests are well-suited to the demands and rewards of the logistics industry.
For those interested in exploring logistics further, the next steps involve seeking out educational opportunities in logistics or supply chain management, connecting with professionals in the field, and gaining hands-on experience through internships or entry-level positions. Engaging with relevant professional organizations and attending industry events can also provide valuable insights and networking opportunities.
In sum, the logistics persona is characterized by a unique combination of adaptability, analytical prowess, problem-solving capabilities, and a keen interest in innovation and sustainability. Aligning your personal attributes and professional interests with the demands of the logistics sector is crucial for finding fulfillment and success in this dynamic field. A career in logistics offers not just the potential for competitive salaries and job stability but also the opportunity to make a significant impact on the efficiency of global trade and the sustainability of supply chains.
For readers considering a logistics career, this exploration underscores the importance of self-assessment and proactive career planning. The logistics industry, with its rapid pace of change and reliance on technology and innovation, presents endless possibilities for personal and professional growth. Whether you’re just embarking on your career journey or seeking a new path, logistics offers a challenging yet rewarding landscape for those ready to dive in and navigate its complexities. Embrace the opportunities to contribute to an industry that is essential to the global economy and poised for continued growth and transformation.
-
The Role of IoT Sensors in Enhancing Freight Visibility
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors into the logistics and freight industry marks a significant leap towards modernizing and optimizing the way goods are monitored and managed across global supply chains. IoT sensors, sophisticated devices capable of capturing and transmitting data in real-time, have become instrumental in revolutionizing freight visibility. They offer an unparalleled ability to track and monitor cargo, providing logistics operators with instant insights into the location, condition, and security of their shipments.
The evolution of freight visibility has been dramatic. Historically, tracking methods were predominantly manual, relying on physical checks and paper-based systems that were both time-consuming and prone to error. This traditional approach offered limited visibility, often resulting in inefficiencies, lost shipments, and a lack of control over the logistics process. The advent of IoT technology has shifted this paradigm, enabling automated systems that offer real-time, accurate tracking and monitoring capabilities.
This article aims to explore the transformative impact of IoT sensors on freight visibility. We will delve into the types of IoT sensors commonly deployed in the logistics sector, discuss the myriad benefits they bring to freight operations, and highlight how they are enhancing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Our objective is to provide insights into how businesses in the logistics and freight industry can leverage IoT sensor technology to gain a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced market environment.
Understanding IoT Sensors in Freight Logistics
What are IoT Sensors?
IoT sensors are a cornerstone of the digital transformation in the freight logistics sector. These devices collect data from their environment and transmit it wirelessly to a central system for analysis. In the context of freight logistics, IoT sensors such as GPS trackers, temperature monitors, and cargo sensors play a pivotal role. GPS trackers provide real-time location data, enabling precise tracking of shipments across the globe. Temperature monitors are crucial for maintaining the integrity of perishable goods, ensuring that they are stored and transported within safe temperature ranges. Cargo sensors can detect and alert logistics operators to unauthorized access or tampering, enhancing the security of shipped goods.
Benefits of Enhanced Freight Visibility
The adoption of IoT sensors in freight logistics brings a host of advantages, significantly improving the visibility of shipments from origin to destination. Enhanced freight visibility leads to improved asset utilization, as operators can optimize routes and reduce idle times based on real-time data. This visibility also contributes to reduced theft and loss by enabling closer monitoring of cargo and quicker response to any discrepancies or anomalies. Furthermore, IoT sensors help ensure enhanced compliance with regulations, particularly for goods that require specific handling or storage conditions. Perhaps most importantly, the increased transparency and reliability afforded by IoT technology result in better customer service, as clients gain access to accurate, up-to-the-minute information about their shipments.
By leveraging IoT sensors, the freight and logistics industry can overcome traditional challenges of cargo tracking and management, paving the way for more efficient, secure, and customer-centric operations.
Implementing IoT Sensors for Freight Visibility
The deployment of IoT sensors in freight logistics is a critical step towards achieving enhanced visibility and control over cargo movements. Here’s the process of selecting, integrating, and managing IoT sensors to revolutionize freight operations.
Selecting the Right IoT Sensors
Choosing the right IoT sensors for freight logistics involves careful consideration of the specific needs and challenges of your freight operations. Durability is paramount, as sensors must withstand various environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, moisture, and rough handling. Battery life is another crucial factor, especially for long-haul shipments where charging opportunities may be limited. Sensors should have long-lasting batteries to ensure continuous operation throughout the journey. Data transmission capabilities are also essential; sensors must be able to send data in real-time or at specified intervals to provide timely insights into freight status. Selecting sensors that offer a combination of these features will ensure that you can track and monitor your shipments effectively, regardless of the complexities of the logistics chain.
Integration with Existing Systems
For IoT sensors to deliver their full value, they must be seamlessly integrated with existing logistics management systems and software. This integration enables the automatic flow of data from the sensors into the systems where it can be analyzed and acted upon. Best practices for integration include using standardized data formats and protocols to ensure compatibility and employing APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that facilitate smooth data exchange between different systems. It’s also important to conduct thorough testing during the integration process to identify and resolve any technical issues that could disrupt data flow or analytics.
Data Management and Analytics
Effectively managing and analyzing the vast amounts of data generated by IoT sensors is critical for optimizing logistics operations and making informed decisions. Data management involves collecting, storing, and ensuring the quality of the data captured by sensors. This data must then be analyzed to extract actionable insights. Analytics tools can identify patterns, trends, and anomalies in the data, providing logistics operators with the information needed to optimize routes, improve asset utilization, and enhance overall operational efficiency. Employing advanced analytics, including predictive analytics, can further enhance decision-making by forecasting future trends and enabling proactive management of potential issues.
Navigating the Future of Freight with IoT
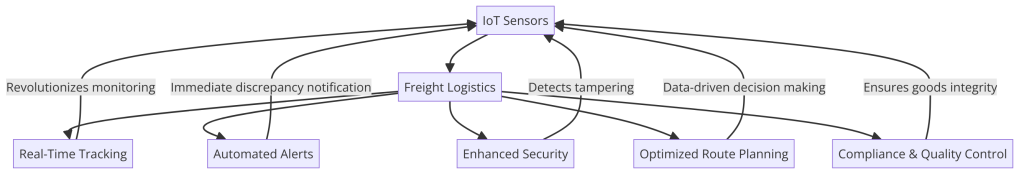
“This diagram displays how IoT sensors revolutionize freight logistics through enhanced tracking, security, and operational efficiency.” The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors has marked a transformative shift in freight logistics, offering unprecedented visibility and control over the transportation and handling of goods. This graph illustrates the multifaceted impact of IoT sensors, from providing real-time tracking of shipments to enabling automated alerts for discrepancies, enhancing the security of cargo, optimizing route planning based on actionable data, and ensuring compliance and quality control for sensitive shipments.
IoT sensors serve as the foundational technology driving these advancements, capturing and transmitting vital data that logistics operators can use to monitor, manage, and optimize their operations. The benefits extend across the logistics chain, improving operational efficiency, reducing losses and theft, ensuring product integrity, and ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction by delivering reliable and timely information about shipments.
As the logistics and freight industry continues to evolve, the role of IoT sensors will only grow in importance, driving further innovation and efficiency in global supply chains. Embracing this technology is key for companies looking to stay competitive in today’s fast-paced market environment, providing a clear advantage in the management and transportation of goods across the globe.
5 Ways IoT Sensors Are Transforming Freight Logistics
1. Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring
IoT sensors revolutionize freight logistics by providing real-time updates on the location and condition of shipments. This capability enables logistics operators to track their cargo every step of the way, offering unparalleled visibility into the supply chain. Real-time tracking allows for proactive management of shipments, ensuring timely delivery and high levels of customer satisfaction.
2. Automated Alerts and Notifications
IoT sensors play a crucial role in generating automated alerts and notifications for any deviations from planned routes, unexpected delays, or unauthorized access to freight. These alerts enable quick responses to potential issues, minimizing the impact on delivery schedules and cargo security.
3. Enhanced Security and Theft Prevention
Through continuous monitoring, IoT sensors significantly enhance the security of freight by immediately detecting any tampering or unauthorized access. This capability is crucial for preventing theft and ensuring the integrity of the cargo from origin to destination.
4. Optimized Route Planning
The data collected by IoT sensors can be used to optimize delivery routes, improving efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By analyzing traffic patterns, weather conditions, and other relevant factors, logistics operators can determine the most efficient routes, reducing fuel consumption and delivery times.
5. Improved Compliance and Quality Control
IoT sensors ensure compliance with regulations and maintain product quality by monitoring conditions such as temperature and humidity within cargo containers. This is especially important for perishable goods, pharmaceuticals, and other sensitive items, where maintaining specific environmental conditions is critical to preserving product integrity.
Future Directions for IoT in Freight Visibility
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors in freight logistics has already marked a significant shift in how cargo is tracked and managed globally. As we look to the future, the potential for further innovation and enhancement in freight visibility through emerging technologies is vast and exciting.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
The next wave of advancements in IoT for freight logistics is poised to be driven by deeper AI integration and advanced analytics. AI algorithms can analyze data collected by IoT sensors to predict potential delays, optimize routes, and even automate decision-making processes in real-time. Moreover, the fusion of IoT with other technologies like 5G connectivity will enable faster, more reliable data transmission, enhancing the responsiveness of freight tracking systems. Another promising area is the use of blockchain technology to create secure, immutable records of shipments, ensuring transparency and trust among all stakeholders in the supply chain.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Logistics
IoT sensors play a crucial role in promoting sustainability and eco-friendly logistics practices. By providing real-time data on vehicle locations and conditions, IoT enables logistics companies to optimize routes, thus reducing fuel consumption and carbon emissions. Additionally, sensors monitoring cargo conditions can help reduce waste by ensuring that goods, especially perishables, are stored and transported under optimal conditions, minimizing spoilage.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite the clear benefits, the widespread adoption of IoT sensor technology in freight logistics faces several challenges. Scalability, cost, and interoperability with existing systems are significant hurdles. To overcome these, the industry needs scalable IoT platforms that can be cost-effectively implemented across diverse logistics operations. Developing standardized protocols for IoT communication can enhance interoperability, making it easier to integrate sensors with different freight management systems. Additionally, fostering partnerships between technology providers, logistics companies, and regulators can help address these challenges and drive the adoption of IoT in freight logistics.
FAQs on IoT Sensors in Freight Logistics
How do IoT sensors enhance freight visibility?
IoT sensors provide real-time data on the location and condition of cargo, significantly enhancing freight visibility. This allows logistics companies to monitor their shipments continuously, make informed decisions quickly, and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
What types of IoT sensors are most beneficial for freight logistics?
GPS trackers for real-time location monitoring, temperature and humidity sensors for condition-sensitive goods, and door sensors for security are among the most beneficial IoT sensors for freight logistics.
Can IoT sensors integrate with all types of freight management systems?
While integration capabilities can vary, many modern IoT sensors are designed with interoperability in mind. They can often be integrated with various freight management systems through APIs and standardized data formats.
What are the main challenges in implementing IoT sensors in freight operations?
Challenges include the initial cost of deployment, ensuring the scalability of IoT solutions, achieving interoperability with existing logistics systems, and managing the vast amounts of data generated by the sensors.
In Conclusion
The transformative impact of IoT sensors on enhancing freight visibility cannot be overstated. From providing unprecedented real-time tracking capabilities to enabling more sustainable logistics practices, IoT technology has fundamentally changed the landscape of freight logistics. As we look forward, the integration of AI, advanced analytics, and other emerging technologies with IoT sensors promises even greater advancements, offering solutions to current challenges and opening up new possibilities for efficiency, security, and customer satisfaction. The adoption of IoT sensor technology in the freight and logistics industry is not just a trend but a necessary evolution to meet the demands of a rapidly changing global market. Embracing continuous innovation and adaptation will be key for logistics companies aiming to stay ahead in this dynamic environment.
-
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Predictive Maintenance for Logistics

Predictive maintenance represents a significant leap forward in how businesses approach the upkeep of machinery and equipment. By utilizing artificial intelligence (AI), this advanced strategy forecasts when maintenance should be performed based on real-time data and predictive analytics, shifting away from traditional schedules based on average lifespans or routine checks. In the logistics industry, where the smooth operation of vehicles, machinery, and systems is crucial, AI-driven predictive maintenance can dramatically transform efficiency, reduce operational costs, and ensure reliability.
The journey from reactive to preventive, and now to predictive maintenance, mirrors the broader technological evolution within the logistics sector. Initially, maintenance was performed only after a failure had occurred (reactive maintenance) or at predetermined intervals regardless of need (preventive maintenance). However, these strategies often led to unnecessary downtime or unexpected breakdowns. The advent of AI and data analytics has paved the way for predictive maintenance, a proactive approach that anticipates issues before they disrupt operations.
This article delves into the transformative potential of AI-driven predictive maintenance within logistics. We aim to explore how leveraging AI not only enhances operational efficiency and reduces costs but also significantly improves the reliability of logistics operations. Through insights into the implementation and benefits of AI in maintenance strategies, businesses in the logistics sector can gain actionable guidance on adopting these advanced practices.
The Evolution of Maintenance Strategies in Logistics
From Reactive to Predictive
Historically, the logistics industry relied on reactive maintenance, addressing equipment failures as they occurred. This approach often resulted in unexpected downtime, affecting delivery schedules and operational efficiency. Transitioning to preventive maintenance, where actions were taken based on predetermined schedules, helped reduce unexpected breakdowns but did not account for the actual condition of the equipment, leading to unnecessary maintenance activities and costs. The advent of predictive maintenance, enabled by AI and data analytics, marks a significant shift towards a more efficient, data-driven approach. By predicting equipment failures before they happen, businesses can plan maintenance more effectively, minimizing downtime and extending the lifespan of their assets.
The Advent of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance utilizes a combination of AI, machine learning, and IoT technology to monitor the condition of equipment in real-time. By analyzing data from sensors and using AI to interpret this information, logistics companies can identify patterns and predict potential failures before they occur. This approach allows for maintenance to be scheduled at the most opportune time, preventing unexpected breakdowns and optimizing the maintenance process.
Understanding AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance
Definition and Core Concepts
AI-driven predictive maintenance goes beyond traditional maintenance strategies by employing advanced data analytics, machine learning algorithms, and IoT integration. This approach analyzes data collected from various sensors attached to equipment to predict when maintenance should be performed. Key components include real-time data collection, predictive analytics models that learn from data over time, and seamless integration with existing logistics systems to trigger maintenance actions when needed.
Benefits for Logistics
The adoption of AI-driven predictive maintenance in logistics brings several significant advantages. Firstly, it minimizes downtime by ensuring that vehicles and machinery are only taken offline for maintenance when necessary, based on predictive insights rather than fixed schedules or unexpected failures. This leads to extended equipment life, as potential issues are addressed before they can cause significant damage. Additionally, the safety of logistics operations is enhanced, as the risk of accidents due to equipment failure is greatly reduced. Overall, AI-driven predictive maintenance supports a more efficient, cost-effective, and reliable logistics operation, setting a new standard in how maintenance is approached within the industry.
Implementing AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance in Logistics
Implementing AI-driven predictive maintenance within the logistics industry represents a strategic move towards enhancing operational efficiency and equipment reliability. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how businesses can integrate this advanced approach into their maintenance strategies.
Assessment and Planning
The initial step towards adopting AI-driven predictive maintenance involves a comprehensive assessment of current maintenance practices. This phase is crucial for identifying the strengths and weaknesses of existing systems and pinpointing areas where AI technologies can make the most significant impact. Companies should evaluate their maintenance history, including downtime statistics, repair costs, and failure rates, to understand where predictive maintenance can offer improvements. Planning involves setting clear objectives for the AI implementation, such as reducing downtime, extending equipment lifespan, or improving safety. It also requires a roadmap for integration, detailing timelines, budget allocations, and personnel involved.
Technology Integration
Selecting the right AI tools and technologies is essential for a successful predictive maintenance program. Companies should look for AI platforms and solutions specifically designed for predictive maintenance, with strong capabilities in data analytics, machine learning, and IoT integration. The integration process involves connecting these AI tools with existing logistics systems and IoT devices installed on equipment and vehicles. This might require hardware upgrades or the installation of additional sensors to ensure comprehensive data collection. Seamless integration allows for the continuous flow of data from logistics operations to the AI system, enabling real-time analysis and insights.
Training and Skills Development
Implementing AI-driven predictive maintenance is not solely a technological challenge; it also requires a skilled workforce capable of managing and interpreting AI-driven systems. Upskilling existing staff through training programs on AI and predictive maintenance is crucial. This training should cover the basics of AI and data analytics, as well as specific instructions on operating the new systems, interpreting data outputs, and taking action based on AI recommendations. Developing these competencies ensures that the workforce can effectively utilize AI-driven predictive maintenance tools, contributing to smoother implementation and better results.
Revolutionizing Maintenance in Logistics with AI
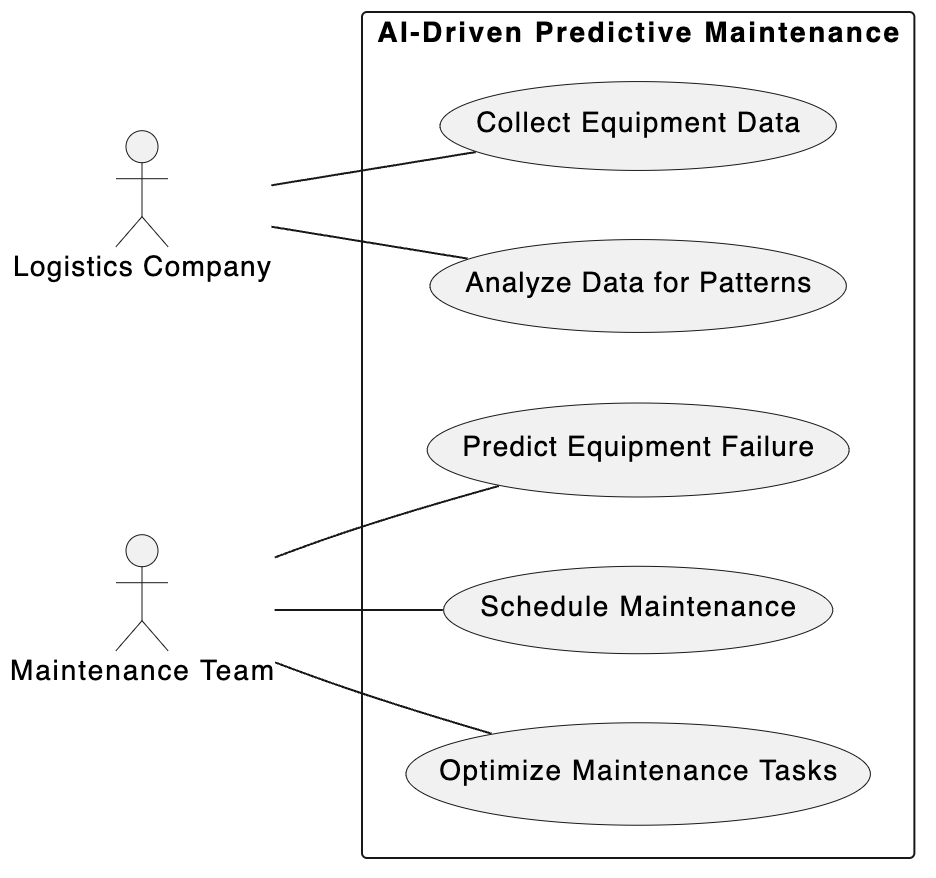
“This use-case diagram outlines the process of AI-driven predictive maintenance in logistics, from data collection to maintenance optimization.” Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the landscape of maintenance strategies within the logistics sector, shifting the paradigm from reactive and preventive maintenance to predictive maintenance. This use-case diagram presents a clear, structured overview of the predictive maintenance process, initiated by logistics companies collecting equipment data. The maintenance team, leveraging AI and machine learning algorithms, analyzes this data to identify patterns indicative of potential equipment failures. This proactive approach enables the prediction of equipment failures before they occur, allowing for the scheduling of maintenance activities at the most opportune times and optimizing maintenance tasks to minimize downtime and extend equipment life.
This AI-driven methodology not only enhances operational efficiency but also significantly reduces costs associated with unexpected equipment failures and maintenance. By ensuring that vehicles and machinery are maintained based on actual condition rather than predefined schedules, logistics operations can achieve higher reliability and performance, contributing to overall supply chain resilience.
Adopting AI-driven predictive maintenance represents a forward-thinking strategy for logistics companies aiming to modernize their operations and maintain competitive advantage in the dynamic global market. Through intelligent data analysis and predictive analytics, logistics companies can look forward to a future where downtime is minimized, and operational efficiency is maximized, all while ensuring the safety and reliability of their operations.
5 Key Components of AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance
1. Data Collection and Management
At the core of AI-driven predictive maintenance is the collection and management of vast amounts of data. IoT devices play a pivotal role in this process, gathering real-time data from various points across logistics operations. This data can include temperature readings, vibration measurements, usage times, and more, providing a comprehensive view of equipment condition. Effective data management practices are essential to organize, store, and process this information, preparing it for analysis by AI algorithms.
2. Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms are the intelligence behind AI-driven predictive maintenance. These algorithms analyze the collected data to identify patterns and anomalies indicative of potential equipment failures. Over time, as the algorithms are exposed to more data, they become increasingly accurate in predicting when maintenance should be performed. This continuous learning process is what sets AI-driven predictive maintenance apart, enabling proactive maintenance actions that can prevent downtime and extend equipment life.
3. Visualization Tools
Visualization tools such as dashboards and visual analytics platforms are crucial for making the data and insights generated by AI algorithms accessible and actionable. These tools present complex data in an easily understandable format, allowing maintenance teams to monitor equipment health in real-time, identify trends, and make informed decisions quickly. Visualization also facilitates communication across teams, ensuring that everyone involved has access to up-to-date information about equipment status and maintenance needs.
4. Automated Alerts and Workflows
A key advantage of AI-driven predictive maintenance is its ability to automate alerts and maintenance workflows. Once the AI system identifies a potential issue, it can automatically notify maintenance personnel and even schedule maintenance tasks. This automation ensures that maintenance actions are taken promptly, reducing the risk of equipment failure. Automated workflows can also help in resource planning, ensuring that the necessary personnel, tools, and parts are available when maintenance is scheduled.
5. Continuous Improvement and Optimization
AI-driven predictive maintenance is not a set-and-forget solution; it requires continuous improvement and optimization. Leveraging AI, companies can regularly refine their predictive models based on new data, feedback from maintenance teams, and evolving operational needs. This process of continuous improvement ensures that the predictive maintenance system remains effective over time, adapting to changes in equipment, operations, and external conditions.
Implementing AI-driven predictive maintenance in logistics is a complex but rewarding endeavor. By following these steps and focusing on the key components, companies can harness the power of AI to revolutionize their maintenance strategies, resulting in increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved reliability.
Future Trends in AI and Predictive Maintenance
The intersection of artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive maintenance is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of innovative logistics operations. As we look to the future, several emerging technologies and methodologies stand out for their potential to redefine how predictive maintenance is implemented in the logistics sector.
Emerging Technologies
The future of AI-driven predictive maintenance in logistics is bright, with several emerging technologies set to enhance its capabilities further. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are poised to offer maintenance technicians immersive training and troubleshooting experiences, allowing them to visualize problems and solutions in real-time. Edge computing is another technology that promises to reduce latency in data processing, enabling faster and more reliable predictive maintenance decisions. Additionally, the development of more sophisticated machine learning algorithms will improve the accuracy of failure predictions, making maintenance schedules even more precise.
Integrating AI with Sustainability Goals
AI-driven predictive maintenance aligns closely with the growing emphasis on sustainability within the logistics industry. By optimizing maintenance schedules, AI helps reduce waste associated with over-maintenance and ensures that equipment operates at peak efficiency, minimizing energy use and emissions. Furthermore, predictive maintenance can extend the lifespan of logistics equipment, promoting a more sustainable approach to resource utilization. Companies are now recognizing that integrating AI with their sustainability goals not only benefits the environment but also enhances their operational efficiency and brand reputation.
Challenges and Opportunities
Adopting AI for maintenance in logistics is not without its challenges. The initial investment in technology and training can be significant, and there may be resistance to change within organizations accustomed to traditional maintenance practices. However, these challenges present opportunities for innovation and growth. Overcoming resistance through education and demonstrating the value of AI-driven approaches can lead to more adaptable and resilient logistics operations. Moreover, the data generated through AI-driven maintenance can provide valuable insights into other areas of the business, opening up new avenues for optimization and improvement.
FAQs on AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance in Logistics
How does AI-driven predictive maintenance differ from traditional maintenance approaches?
AI-driven predictive maintenance utilizes data, algorithms, and machine learning to predict when equipment will require maintenance before a failure occurs. This approach contrasts with traditional methods that rely on set schedules or responding after a breakdown, leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime.
What are the initial steps for implementing AI in predictive maintenance strategies?
The initial steps include conducting a thorough assessment of current maintenance practices, identifying key areas for improvement, selecting appropriate AI and IoT technologies, and training staff to manage and interpret AI-driven systems effectively.
Can small logistics companies afford AI-driven predictive maintenance?
Yes, small logistics companies can afford AI-driven predictive maintenance. Many scalable solutions on the market can be customized to fit various budgets and operational sizes. The key is to start small, perhaps by focusing on critical equipment, and gradually expand as the benefits become evident.
How does AI-driven predictive maintenance impact the workforce in logistics?
AI-driven predictive maintenance can significantly enhance the workforce by reducing the physical strain of emergency repairs, improving safety, and offering opportunities for upskilling. Employees can transition from performing routine maintenance tasks to more strategic roles, overseeing AI systems and focusing on continuous improvement initiatives.
In Conclusion
The integration of AI in predictive maintenance represents a pivotal shift towards more efficient, reliable, and sustainable logistics operations. Through the adoption of emerging technologies, alignment with sustainability objectives, and the overcoming of initial challenges, the logistics sector stands on the brink of a transformative era. AI-driven predictive maintenance not only promises reduced downtime and operational costs but also offers a path to eco-friendly practices that can bolster a company’s reputation and market position. As the logistics industry continues to evolve, embracing AI-driven predictive maintenance will be crucial for companies aiming to stay competitive in an increasingly complex and fast-paced global market.
-
The Role of Nanotechnology in the Future of Logistics Solutions

In the dynamic world of logistics, a groundbreaking innovation is making waves: nanotechnology. This advanced technology, operating at the molecular and atomic levels, is poised to revolutionize the logistics industry. Nanotechnology, with its ability to manipulate materials at the nanoscale, offers unprecedented solutions, reshaping how we think about and manage logistics processes. From enhanced packaging materials to advanced tracking systems, the potential of nanotechnology in logistics is vast and varied.
Nanotechnology stands as a game-changer in logistics. It promises not only to optimize current processes but also to open doors to entirely new methods of operation. Its impact is expected to be transformative, offering solutions that are more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective. This article aims to delve into the fascinating world of nanotechnology in logistics. We will explore the basics of nanotechnology, its current applications in the industry, and its potential to shape the future of logistics. By understanding the scope and capabilities of nanotechnology, we can gain insight into how it will redefine logistics solutions, making them more adaptable to the challenges of the modern world.
Nanotechnology in Logistics: A Deep Dive
Basics of Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology involves the manipulation and use of materials at the nanoscale, where unique phenomena enable novel applications. In logistics, this technology offers transformative possibilities due to its ability to alter material properties, leading to lighter, stronger, and more durable materials. Understanding these fundamental aspects is key to comprehending how nanotechnology can revolutionize logistics operations, from warehousing and transportation to packaging and delivery.
Current Applications in Logistics
Nanotechnology is already making significant inroads in logistics. One of the most notable applications is in the realm of packaging. Nanotech-enhanced materials can provide superior protection for goods, extending shelf life and reducing damage during transit. Additionally, the use of nanosensors in tracking and monitoring provides a new level of precision and efficiency in supply chain management. These sensors can monitor conditions like temperature and humidity in real-time, ensuring the integrity of sensitive products throughout their journey.
The Future of Nanotech in Logistics
Looking ahead, the potential applications of nanotechnology in logistics are boundless. We are on the cusp of seeing more advanced uses of nanotech, such as in the creation of self-healing materials, further reducing the costs and challenges associated with damaged goods. Nanotechnology could also revolutionize transportation, leading to lighter yet stronger vehicles and containers, significantly reducing fuel consumption and emissions. As research and development in this field continue to accelerate, the logistics industry stands on the brink of a nanotechnology-driven transformation, promising to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and resilience in the face of ever-evolving global challenges.
Integrating Nanotechnology into Logistics
Integrating nanotechnology into logistics requires a strategic and methodical approach. The first step involves a thorough evaluation of your logistics operations to identify specific challenges that nanotechnology can address. This might include issues like packaging durability, spoilage, or inefficiency in tracking systems. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of current nanotechnology solutions is crucial in this phase. For instance, if product longevity is a concern, nanotech-enhanced packaging could be a solution.
The next stage is developing a strategy for implementation. This often begins with research and development, possibly in collaboration with nanotechnology experts, to create solutions tailored to your unique logistics needs. For instance, if tracking accuracy is a problem, developing custom nano-sensors might be a viable solution. Before a full-scale implementation, it is prudent to conduct pilot tests to evaluate the practicality and effectiveness of these solutions in real-world logistics scenarios.
Integration with existing systems is a critical consideration. The new nanotechnology solutions should seamlessly fit into your existing logistics infrastructure, which might necessitate technological upgrades or process adjustments. Alongside this, there is a need for comprehensive training for your logistics team to ensure they can effectively utilize and maintain the new nanotechnology solutions. Lastly, staying informed and compliant with the regulatory landscape regarding nanotechnology is crucial, especially for solutions that interact directly with products.
The Transformative Impact of Nanotechnology in Modern Logistics
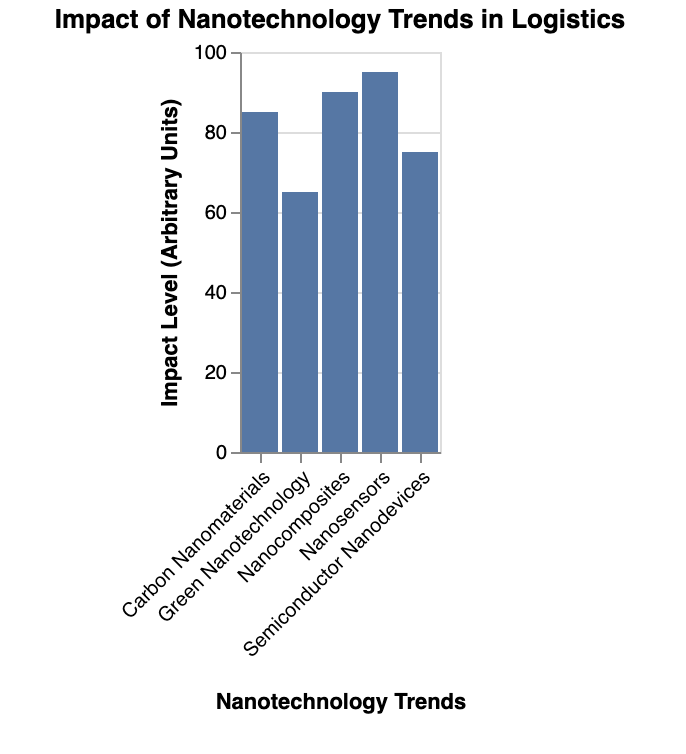
The bar chart above illustrates the impact level of various nanotechnology trends in the logistics industry. The categories include Carbon Nanomaterials, Semiconductor Nanodevices, Green Nanotechnology, Nanocomposites, and Nanosensors. In the ever-evolving landscape of logistics, nanotechnology emerges as a key innovator, promising to redefine the industry’s future. This section delves into the specific trends of nanotechnology shaping logistics, as highlighted in the accompanying bar chart.
Carbon Nanomaterials: Exhibiting the highest impact, these materials, including graphene and carbon nanotubes, offer unparalleled strength and flexibility. Their application in logistics could lead to more resilient packaging materials, reducing damage during transportation and extending the shelf life of products.
Semiconductor Nanodevices: These devices play a significant role in enhancing computational capabilities essential for logistics operations. Their impact is notable in developing advanced tracking systems and optimizing route planning for shipments.
Green Nanotechnology: With a focus on sustainability, this trend is crucial in developing eco-friendly logistics solutions. From biodegradable packaging materials to recycling processes, green nanotechnology is pivotal in reducing the industry’s environmental footprint.
Nanocomposites: These materials are particularly significant in creating lightweight yet durable components for logistics vehicles and containers, significantly boosting transportation efficiency and reducing fuel consumption.
Nanosensors: Ranking highest in impact, nanosensors bring a new level of precision to logistics. Their application in real-time tracking and environmental monitoring ensures the integrity and timely delivery of goods, revolutionizing supply chain management.
The integration of these nanotechnology trends is not just about adopting cutting-edge solutions; it represents a stride towards more efficient, secure, and sustainable logistics operations. As these innovations continue to evolve, their potential to transform the logistics industry becomes increasingly tangible, promising a future that is smarter, more resilient, and more responsive to the changing demands of the global market.
Top Innovations in Nanotechnology for Logistics
- Advanced Nano-Materials for Packaging: Nanotechnology is revolutionizing packaging in logistics with the development of materials that are not only more durable but can also react to environmental changes. These advanced materials can enhance product protection, extend shelf life, and include smart features like embedded nano-sensors for continuous quality monitoring.
- Nano-Sensors for Enhanced Tracking: The introduction of nano-sensors in logistics has brought about a paradigm shift in tracking and monitoring. These sensors provide real-time, precise data on a variety of metrics including location, temperature, and humidity, vastly improving the accuracy and reliability of supply chain management.
- Nano-Based Logistics Automation: Automation in logistics processes is getting a boost from nanotechnology. Nano-enhanced systems are being developed to streamline operations, reduce errors, and increase overall efficiency.
- Improved Transportation Materials: Nanotechnology is being leveraged to create lighter, stronger materials for transportation vehicles. This advancement not only reduces fuel consumption but also allows for greater payload capacity, making transportation more efficient and cost-effective.
- Nano-Enabled Security Solutions: In the realm of logistics security, nanotechnology offers innovative solutions like tamper-evident seals and traceable nano-tagging. These applications enhance the safety and traceability of goods throughout the supply chain.
- Self-Healing Materials: Future advancements in nanotechnology may introduce materials capable of repairing themselves. This innovation could significantly reduce maintenance costs and extend the life of transportation and packaging materials.
- Energy-Efficient Operations: Nano-enhanced materials and systems can contribute to more energy-efficient logistics operations, reducing the carbon footprint and aligning with sustainability goals.
- Wearable Nano-Devices for Personnel: Implementing wearable nano-devices for logistics personnel could streamline operations. These devices can monitor health and safety, ensure protocol compliance, and enhance communication within the logistics network.
- Smart Warehousing Solutions: Nanotechnology can transform warehousing operations with smart shelving and storage solutions that optimize space usage and improve inventory management.
- Nano-Structured Surfaces for Easier Transportation: The development of nano-structured surfaces can reduce friction and wear-and-tear in transportation, leading to smoother logistics operations and extended lifespan of vehicles and equipment.
The integration of nanotechnology into logistics is not just about adopting new technologies; it represents a significant leap towards smarter, more efficient, and more sustainable logistics operations. As these innovations continue to evolve and mature, their potential to transform the logistics industry becomes increasingly evident.
Nanotechnology and the Future of Logistics
Emerging Trends in Nanotech and Logistics
The integration of nanotechnology in logistics is ushering in a new era of innovation and efficiency. One of the emerging trends is the development of nano-materials for transportation and packaging, which are not only stronger and lighter but also have smart capabilities like temperature regulation and damage detection. Another trend is the use of nano-sensors, which are revolutionizing tracking, monitoring, and maintaining the integrity of goods throughout the supply chain. Additionally, advancements in nano-robotics are expected to play a significant role in automating and streamlining logistics operations, especially in warehousing and inventory management.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
Despite its potential, the adoption of nanotechnology in logistics faces several challenges. The high cost of development and integration poses a significant barrier, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises. There’s also the challenge of ensuring that nano-enabled logistics solutions are compatible with existing systems. To overcome these obstacles, partnerships between logistics companies and nanotech firms are crucial. These collaborations can facilitate shared R&D efforts, cost-sharing, and the creation of interoperable solutions.
Sustainability and Efficiency
Nanotechnology holds great promise in enhancing sustainability and efficiency in logistics. Nano-enhanced materials can reduce the weight of transportation vehicles, leading to lower fuel consumption and emissions. Nano-sensors can help in optimizing routes and reducing energy usage. Moreover, the durability of nano-materials can lead to a decrease in waste, contributing to more sustainable logistics practices.
FAQs on Nanotechnology in Logistics
How does nanotechnology improve the efficiency of logistics operations?
Nanotechnology enhances efficiency through the development of stronger, lighter materials for transportation, advanced tracking with nano-sensors, and automation with nano-robotics.
What are the sustainability benefits of using nanotechnology in logistics?
Nanotechnology contributes to sustainability by enabling the creation of more durable materials, reducing waste, and optimizing energy usage in transportation and warehousing.
Are there any risks associated with using nanotechnology in logistics?
Potential risks include environmental and health concerns related to the disposal of nano-materials and the need for strict regulatory compliance to ensure safe usage.
Expert Insights and Practical Tips
Expert Insight: When considering nanotechnology for logistics, focus on long-term benefits like sustainability and efficiency gains. Start with pilot projects to understand its impact on your operations.
Practical Tip: Stay informed about the latest developments in nanotechnology and logistics. Collaborate with experts in the field to explore innovative solutions tailored to your specific needs.
In conclusion, the integration of nanotechnology in logistics represents a monumental shift towards a more efficient, secure, and sustainable future. From advanced materials for packaging and transportation to nano-sensors for precise tracking, the possibilities are vast and transformative. The challenges in adoption, while significant, can be navigated through strategic partnerships and a focus on long-term benefits. The pioneering spirit in embracing nanotechnology will not only redefine logistics operations but also set new standards for innovation, efficiency, and sustainability in the industry. As we continue to explore and implement these nano-enhanced solutions, the future of logistics looks brighter, smarter, and more resilient.
-
Strategies for Implementing Sustainable Freight Solutions

In an era where environmental concerns are not just buzzwords but imperatives for survival, the logistics and transportation sector stands at a crucial juncture. The urgency to shift towards sustainable freight solutions has never been more pronounced. As the backbone of global trade and commerce, this sector has the unique opportunity to pave the way for a greener, more sustainable future. Sustainable freight is no longer a choice but a necessity, emerging as a key player in the fight against climate change and environmental degradation. This shift not only promises a healthier planet but also ensures the longevity and resilience of the logistics industry itself.
Currently, the freight transport sector is a significant contributor to global carbon emissions, accounting for a substantial portion of the world’s greenhouse gas outputs. Traditional freight methods, heavily reliant on fossil fuels, present a myriad of environmental challenges. These include air pollution, excessive carbon footprints, and a considerable strain on natural resources. The repercussions of these practices are far-reaching, affecting not just the environment but also the health and well-being of populations worldwide. In response to these daunting challenges, the industry is standing at a crossroads, with sustainable practices not just being a moral choice, but a strategic imperative for survival and growth.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on transitioning to sustainable freight solutions. We will delve into actionable strategies and innovative solutions that can revolutionize freight transport, making it more environmentally friendly and efficient. Our journey will encompass a thorough understanding of what constitutes sustainable freight, the environmental impacts of current practices, and the economic and social advantages of adopting greener methods. By the end of this article, readers will have a deeper understanding of sustainable freight and be equipped with the knowledge to implement these practices in their own operations, contributing to a more sustainable and prosperous future for all.
Understanding Sustainable Freight
Definition and Importance
Sustainable freight refers to the implementation of environmentally friendly practices in the logistics and transportation sector. This concept goes beyond merely reducing emissions; it encompasses a holistic approach that includes efficient resource utilization, minimizing ecological footprints, and fostering a balance between economic growth and environmental stewardship. Adopting sustainable freight practices is crucial for the health of our planet. It mitigates the adverse effects of climate change, reduces pollution, and conserves natural resources. From a business perspective, sustainable freight is not just about corporate responsibility; it’s a strategic decision that can lead to increased efficiency, cost savings, and a stronger, more positive brand image in the eyes of consumers.
Environmental Impact of Traditional Freight Methods
The traditional freight methods, dominated by diesel-powered vehicles and energy-intensive operations, pose significant environmental challenges. These methods are major contributors to air pollution, emitting particulate matter and nitrogen oxides that harm air quality and public health. The carbon emissions from these vehicles contribute significantly to climate change, leading to rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, and disruptions in ecosystems. Additionally, the conventional freight methods are resource-intensive, often leading to excessive energy consumption and wastage. The ecological footprint extends beyond just emissions; it encompasses the entire supply chain, from packaging materials to the energy used in warehouses and distribution centers.
The Economic and Social Benefits of Sustainable Freight
Transitioning to sustainable freight solutions is not just environmentally responsible; it’s economically sensible and socially beneficial. Companies adopting green logistics practices often experience cost savings in the long term through improved fuel efficiency, reduced energy costs, and optimized supply chain management. Sustainable practices can lead to a leaner, more efficient operation, reducing waste and unnecessary expenses. From a social perspective, companies that prioritize sustainability often see improved brand loyalty and customer trust. They are viewed as responsible corporate citizens, contributing to their communities and the planet. Furthermore, sustainable freight practices can lead to healthier work environments and communities by reducing pollution and its associated health risks, fostering a better quality of life for everyone involved.
Implementing Sustainable Practices in Freight Operations
Assessment of Current Freight Practices
The first step towards sustainability in freight operations is a thorough assessment of current practices. This evaluation involves scrutinizing every aspect of your freight operations, from the fuel your vehicles use to the efficiency of your logistics routes. Key areas to focus on include fuel consumption, emission levels, route optimization, packaging methods, and overall supply chain efficiency. Conducting a comprehensive carbon footprint analysis of your current operations can highlight areas with the highest environmental impact. It’s essential to identify not just the obvious areas, but also the less apparent ones, such as the energy efficiency of your warehouses or the sustainability of your supply sources.
Strategies for Sustainable Transformation
Once the assessment is complete, the next step is implementing sustainable strategies. This transformation can be approached systematically:
Route Optimization: Utilize advanced routing software to plan the most efficient routes, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. This also involves consolidating shipments to maximize load efficiency.
Eco-friendly Vehicles: Transition to green vehicles, such as electric or hybrid trucks, which significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Investing in newer, more fuel-efficient vehicles can also make a substantial difference.
Energy-Efficient Warehouses: Upgrade warehouses with energy-saving technologies like solar panels, LED lighting, and smart heating and cooling systems. Implementing energy management systems can further optimize energy usage.
Employee Training: Educate and train employees on sustainable practices, emphasizing the importance of eco-friendly operations and how they can contribute on an individual level.
Technology and Innovation in Sustainable Freight
In the realm of sustainable freight, technology plays a pivotal role. Innovations such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain are revolutionizing how freight operations are managed:
- AI and Machine Learning: These technologies can predict optimal routes, manage inventory efficiently, and reduce idle time for vehicles.
- IoT Devices: IoT can track vehicle performance, monitor fuel usage, and provide real-time data for better decision-making.
- Blockchain: This technology ensures transparency and accountability in the supply chain, from the origin of goods to their final delivery, ensuring sustainable practices are followed throughout.
Analyzing Sustainable Freight Practices Adoption

This pie chart depicts the adoption percentages of sustainable freight practices, highlighting electric trucks at 40%, renewable energy in warehousing at 25%, eco-friendly packaging at 20%, and route optimization at 15%. The pie chart provides a clear visual breakdown of how different sustainable freight practices are being adopted within the logistics industry.
Leading the Green Revolution: Electric Trucks
Electric trucks, comprising 40% of the adoption, are at the forefront of sustainable freight. This significant shift towards electric vehicles reflects the industry’s response to environmental concerns and regulatory pressures, driven by their advantages in reducing emissions and operational costs.
Powering Warehouses with Renewable Energy
Renewable energy in warehousing, representing 25% of the adoption, is another key area. The integration of solar panels and other green technologies in logistics operations exemplifies the industry’s efforts to reduce reliance on non-renewable energy sources, thereby minimizing environmental impact and operational costs.
Embracing Eco-Friendly Packaging
With 20% adoption, eco-friendly packaging is a crucial trend. This move towards sustainable packaging solutions, including the use of recycled and biodegradable materials, aligns with the increasing consumer demand for environmentally responsible practices and helps reduce waste significantly.
Route Optimization for Enhanced Efficiency
Lastly, the adoption of route optimization techniques, accounting for 15%, showcases the industry’s commitment to improving efficiency and reducing emissions. Utilizing advanced routing software, logistics companies are able to plan more efficient routes, leading to reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions.
Top 10 Sustainable Freight Practices to Adopt Now
1. Green Vehicles
Adopting electric trucks and hybrid engines is a game-changer in reducing emissions. These vehicles are not only environmentally friendly but also cost-efficient in the long run due to lower fuel and maintenance costs.
2. Carbon Offsetting
Implementing carbon offset programs is a practical approach to compensating for the emissions you can’t eliminate. This involves investing in environmental projects that reduce greenhouse gases.
3. Eco-friendly Packaging
Switching to sustainable packaging reduces waste and environmental impact. This includes using recycled materials and designing packaging to minimize size and weight.
4. Collaborative Logistics
Sharing resources and logistics, such as joint distribution between companies, maximizes efficiency and reduces the total number of trips required, thereby cutting down emissions.
5. Energy-Efficient Routing
Utilizing software to optimize routes not only saves time but also significantly reduces fuel consumption, leading to lower emissions.
6. Driver Training
Educating drivers on eco-driving techniques, such as efficient acceleration and braking, can lead to significant reductions in fuel usage.
7. Renewable Energy Use
Incorporating renewable energy sources like solar or wind power in your operations can drastically reduce your carbon footprint.
8. Waste Reduction
Implementing practices to reduce waste in all areas of your operation, from the office to the warehouse, contributes significantly to environmental sustainability.
9. Regulatory Compliance
Staying up-to-date with environmental regulations and ensuring compliance is crucial for sustainable operations and avoiding legal penalties.
10. Stakeholder Engagement
Engaging stakeholders, including suppliers and customers, in your sustainability efforts can create a more comprehensive and effective approach to green logistics.
By integrating these sustainable practices, businesses can not only contribute to a healthier planet but also enjoy cost savings, enhanced brand reputation, and operational efficiencies. The transition to sustainable freight is an ongoing journey, requiring commitment, innovation, and continuous improvement.
The Future of Freight – Towards a Greener Horizon
The freight and logistics industry stands on the cusp of a significant transformation, driven by a growing awareness of environmental sustainability and technological advancements. The future of freight is being reshaped by innovative trends and a collective move towards more sustainable practices.
Industry Trends and Innovations
Current trends in sustainable freight are heavily influenced by technological innovation and a shift in corporate and consumer values. Electric vehicles are at the forefront of this change, with major companies investing in electric trucks for last-mile delivery. Autonomous vehicles, though still in developmental stages, promise to revolutionize the industry by optimizing routes and reducing fuel consumption. In terms of operational efficiency, the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are enabling smarter and more efficient supply chains. These technologies offer real-time tracking, predictive analytics for maintenance and delivery optimization, and improved inventory management.
Vision for the Future
Looking forward, the vision for sustainable freight is one where green practices are not just an add-on but are integral to logistics operations. This future embraces a circular economy where waste is minimized, and resources are reused, leading to a more sustainable and efficient supply chain. The integration of clean energy sources, like solar and wind, in logistics infrastructure, and the adoption of green materials for packaging and construction are pivotal elements of this vision.
FAQs About Sustainable Freight Solutions
What are the cost implications of implementing sustainable freight solutions?
While the initial investment in sustainable technologies might be higher, they offer long-term savings through reduced fuel costs, lower maintenance expenses, and potential tax incentives.
How effective are sustainable freight practices in reducing environmental impact?
Sustainable freight practices significantly reduce carbon emissions, decrease fuel consumption, and minimize waste, making them highly effective in mitigating environmental impact.
Can sustainable freight solutions be scaled for large operations?
Yes, sustainable solutions are scalable. With advancements in technology and increased availability of sustainable resources, these practices are becoming more feasible for larger operations.
What technologies are available to support sustainable freight?
Technologies such as electric and hybrid vehicles, AI and machine learning for route optimization, IoT for tracking and efficiency, and blockchain for supply chain transparency are pivotal in supporting sustainable freight.
Expert Insights
Industry experts emphasize that the transition to sustainable freight is not just a trend but a necessary evolution of the industry. They highlight the importance of regulatory support, consumer demand, and corporate responsibility in driving this change.
In conclusion, the journey towards sustainable freight is both a challenge and an opportunity. This article has explored various strategies, from the adoption of green vehicles and eco-friendly packaging to leveraging technology for efficient operations. The case studies and trends discussed paint a hopeful picture of a more sustainable and efficient future in freight and logistics. As we move forward, it is imperative for businesses, policymakers, and consumers to collaborate and innovate continuously. The transition to sustainable freight is not just a pathway to environmental stewardship but a strategic move towards long-term economic resilience and success. By embracing these changes, the freight industry can ensure a greener horizon for future generations.
-
Navigating the Challenges of Global Supply Chain Management
In an era where a product’s components can hail from multiple continents and be assembled miles away, the nuances of global supply chain management are more evident than ever. This intricate network, ensuring seamless goods flow from producers to global consumers, stands as a testament to impeccable coordination, advanced technology, and strategic prowess. Yet, this complexity is not without its challenges. In our interconnected global economy, supply chain management transcends mere logistics, becoming a strategic linchpin that can make or break businesses.
It orchestrates operations across varied geographies, cultures, and regulations, ensuring a coffee aficionado in Seattle savors beans from Ethiopia, or a tech enthusiast in Tokyo gets the latest gadget designed in California and crafted in China. As the digital age propels consumers to seek faster, cheaper, and superior products, businesses are pressed to foster supply chains that are not only efficient but resilient against diverse disruptions, be they political, environmental, or economic.
Understanding the Intricacies of Global Supply Chains
Navigating the world of global supply chains is akin to solving a dynamic puzzle, where each piece impacts several others.
The Multi-Faceted Nature of Global Supply Chains: From Sourcing to Delivery
A product’s journey, from raw material to a consumer’s hands, involves multiple stages—sourcing, manufacturing, distribution, and retail. Each stage, potentially occurring in a different country with its unique challenges, must be meticulously planned and executed.
The Role of Technology, Geopolitics, and Regulations in Shaping Supply Chains
- Technology: Advanced software systems enable real-time tracking, while AI predicts demand surges or lulls. Drones and autonomous vehicles are redefining delivery mechanisms.
- Geopolitics: Trade agreements, diplomatic relations, and regional stability can significantly impact supply routes and costs.
- Regulations: From environmental standards to labor laws, varying regulations across countries can influence where and how products are manufactured.
Key Challenges in Global Supply Chain Management
While the potential rewards of a global supply chain are immense, so are the challenges.
Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Wars Affecting Supply Routes
Trade wars, such as the recent tensions between the U.S. and China, can disrupt established supply routes, impose tariffs, and increase costs. Such geopolitical uncertainties require businesses to be agile, often necessitating the reshuffling of suppliers and manufacturers.
Cultural and Regulatory Differences Across Countries
What’s standard practice in one country might be taboo in another. Understanding and respecting cultural nuances is crucial, especially when negotiating deals or resolving disputes. Similarly, regulatory differences, from safety standards to import duties, can pose challenges. Read More
-
The Role of E-commerce in Shaping Modern Logistics

In the digital age, e-commerce has emerged as a juggernaut, reshaping industries and consumer behaviors alike. With global online sales skyrocketing, the world has witnessed an e-commerce boom that shows no signs of slowing down. This exponential growth, while offering unparalleled convenience to consumers, has also brought to the forefront a critical component of the e-commerce ecosystem: logistics. The intricate dance between e-commerce and logistics is not just a matter of shipping products; it’s about meeting evolving consumer expectations, leveraging technology, and ensuring that the digital promise of “buy now” translates to a tangible “enjoy soon.”
From niche online bookstores in the 90s to today’s e-commerce giants offering everything under the sun, the digital marketplace has expanded beyond imagination. With the convenience of shopping from the comfort of one’s home, coupled with a plethora of choices and seamless digital payment systems, e-commerce has become a preferred shopping method for many.
As e-commerce platforms promise faster deliveries and a wider range of products, the logistics industry has had to evolve rapidly. The challenge isn’t just about moving products but doing so efficiently, timely, and in line with the brand promises made online.
The Evolution of Logistics in the E-commerce Era
The rise of e-commerce has necessitated a paradigm shift in how logistics operates, moving from a traditional B2B model to a more dynamic B2C approach.
How Consumer Demands Have Shifted Logistics from a B2B to a B2C Model
In the past, logistics primarily dealt with bulk shipments, transporting goods between manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers. However, with e-commerce, the focus has shifted to individual consumers. Now, it’s about ensuring that a product reaches a specific individual at a specific location within a stipulated time frame.
The Rise of “Last-Mile Delivery” and Its Challenges
Last-mile delivery refers to the final step in the delivery process, where a product is delivered from a local distribution center to the end consumer. It’s arguably the most crucial and challenging aspect of e-commerce logistics. Challenges include navigating urban landscapes, managing delivery times amidst traffic, ensuring product safety, and meeting consumer expectations of timely delivery.
Technological Innovations Driven by E-commerce
E-commerce’s demands have spurred significant technological advancements in logistics, ensuring operations are efficient, transparent, and consumer-centric. Read More
-
Subscribe
Subscribed
Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.